Break the medical term spondylodynia into its component parts. – Break the medical term spondylodynia into its component parts, revealing the intricate structure and meaning behind this term that describes spinal pain. By dissecting the term into its Greek roots, we uncover the anatomical structures involved and the mechanisms that contribute to this condition, providing a deeper understanding of its causes and potential treatments.
Delving into the etymology and anatomy of spondylodynia, we gain insights into the role of the spine, vertebrae, and intervertebral discs in the development of pain. We explore the underlying pathophysiology, examining the various factors that can lead to spondylodynia, from age-related changes to lifestyle habits and underlying medical conditions.
Definition and Etymology

Spondylodynia, a medical term derived from Greek, refers to pain in the vertebrae, the bones that make up the spinal column. Etymologically, the term “spondylodynia” can be broken down into its component parts:
- “Spondylo” – Greek for “vertebra”
- “Dynia” – Greek for “pain”
Thus, the term “spondylodynia” literally translates to “vertebral pain”.
Anatomical Components
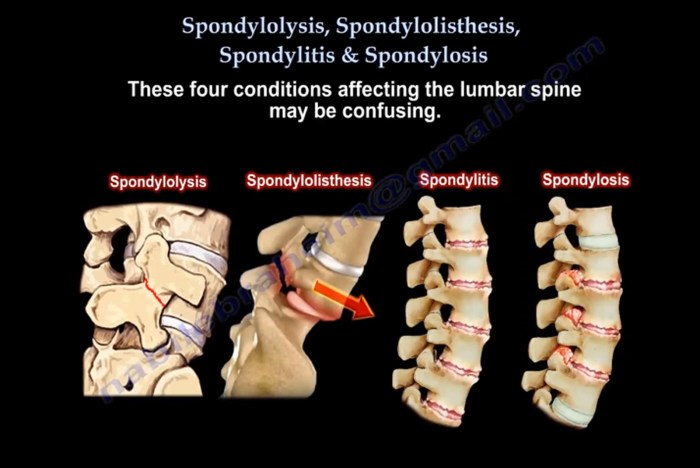
Spondylodynia refers to pain in the vertebrae, which are stacked one upon another to form the spinal column. Each vertebra consists of a body, pedicles, laminae, and processes. The vertebral bodies are the weight-bearing portions of the vertebrae, while the pedicles and laminae form the vertebral arch.
The processes provide attachment points for muscles and ligaments.
Spondylodynia can affect any part of the vertebra, but it is most commonly associated with the lumbar (lower back) and cervical (neck) regions of the spine.
Causes and Pathophysiology: Break The Medical Term Spondylodynia Into Its Component Parts.
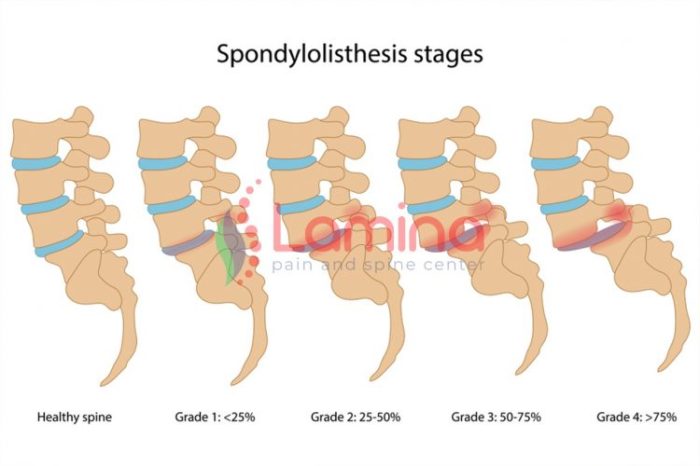
Spondylodynia can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Degenerative changes, such as osteoarthritis and spinal stenosis
- Trauma, such as fractures or dislocations
- Infections, such as osteomyelitis or discitis
- Inflammatory conditions, such as ankylosing spondylitis or rheumatoid arthritis
- Muscle strains or sprains
The underlying mechanisms that lead to pain in spondylodynia vary depending on the cause. For example, in osteoarthritis, the degeneration of cartilage and bone in the spine can lead to inflammation and pain. In spinal stenosis, the narrowing of the spinal canal can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots, causing pain, numbness, and weakness.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the literal meaning of spondylodynia?
Spondylodynia translates to “pain in the vertebrae” from Greek, where “spondylo” refers to vertebrae and “dynia” means pain.
Which anatomical structures are affected by spondylodynia?
Spondylodynia primarily affects the vertebrae, the bones that make up the spinal column, and the intervertebral discs, theクッション-like structures between the vertebrae.
What are the common causes of spondylodynia?
Spondylodynia can result from various causes, including age-related degeneration, spinal injuries, poor posture, obesity, and underlying medical conditions such as arthritis or osteoporosis.