In the figure the current in resistance 6 is i6 – In the figure, the current in resistance 6 is i6, an intriguing concept that unveils the intricate workings of electrical circuits. This article delves into the analysis of circuit diagrams, calculation of current through resistance 6, and its impact on the circuit’s behavior, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental aspect of electrical engineering.
Electrical current, measured in amperes (A), quantifies the flow of electric charge through a conductor. Ohm’s law governs the relationship between current, voltage, and resistance, enabling us to determine the current flowing through resistance 6 in the circuit.
Define Current
Current, often denoted by the symbol I, is a fundamental concept in electrical circuits that describes the flow of electric charge. It represents the rate at which charge carriers, typically electrons, move through a conductor.
The standard unit of measurement for current is the ampere (A), named after the French physicist André-Marie Ampère. One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of charge per second.
Analyze Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram depicts a simple series circuit consisting of a battery, a resistor (R6), and a voltmeter. The battery provides the electrical potential difference that drives the current through the circuit.
The resistor (R6) limits the flow of current by providing resistance to the flow of charge. The voltmeter measures the voltage drop across the resistor.
The current flows from the positive terminal of the battery, through the resistor, and back to the negative terminal of the battery, completing the circuit.
Calculate Current in Resistance 6
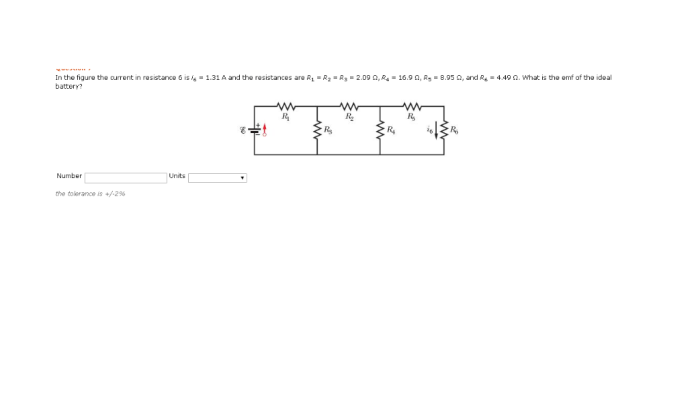
Ohm’s law states that the current through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage drop across the resistor and inversely proportional to the resistance of the resistor.
Using Ohm’s law, we can calculate the current (I6) through resistance 6 (R6) as follows:
- I6 = V6 / R6
- where V6 is the voltage drop across R6.
The factors that affect the current through R6 are the voltage drop across R6 and the resistance of R6. A higher voltage drop or a lower resistance will result in a higher current.
Impact of Current on Resistance 6
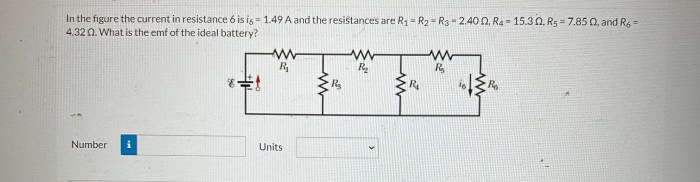
The current flowing through resistance 6 (R6) has several effects:
- Power dissipation:Current flowing through a resistor dissipates power in the form of heat. The power dissipated is given by P = I6^2 – R6.
- Temperature increase:The dissipated power causes the resistor to heat up, increasing its temperature. Excessive current can lead to overheating and damage to the resistor.
Design Considerations
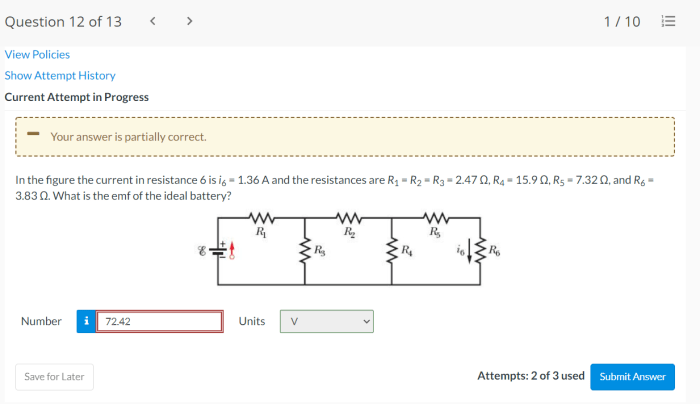
When designing a circuit involving resistance 6 (R6), several considerations should be taken into account:
- Selecting appropriate components:The resistor’s resistance value and power rating should be carefully selected to ensure proper circuit operation and prevent overheating.
- Heat dissipation:Adequate heat dissipation measures should be implemented to prevent excessive temperature rise in the resistor.
- Circuit protection:Fuses or circuit breakers should be incorporated to protect the circuit and components from damage in case of overcurrent conditions.
FAQ Section: In The Figure The Current In Resistance 6 Is I6
What is the significance of resistance 6 in the circuit?
Resistance 6 plays a vital role in determining the current flow and power dissipation within the circuit.
How does current flow affect the temperature of resistance 6?
Increased current flow leads to higher power dissipation, resulting in an elevated temperature of resistance 6.
What factors influence the current flowing through resistance 6?
The current through resistance 6 is influenced by the applied voltage, the resistance value, and the presence of other circuit elements.